
- Mac mysql server start command line how to#
- Mac mysql server start command line code#
- Mac mysql server start command line password#
- Mac mysql server start command line windows#
Mac mysql server start command line code#
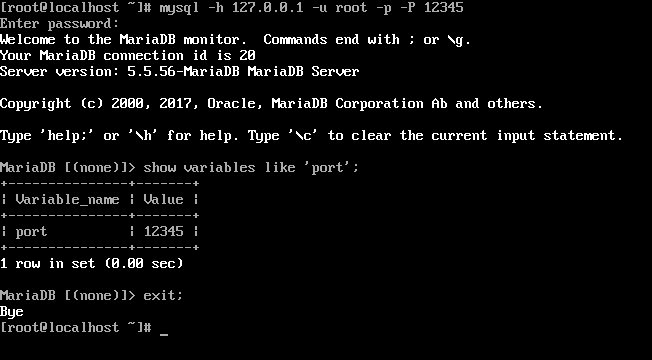
Open terminal/command line interface (CLI) and run below commands. To do this, you just need to connect to your database server (e.g.If enabling “Automatically Start MySQL Server on Startup” does not work then doing below process will fix it. the VS Code SQLTools extension), you need to switch to the "legacy" authentication flow for MySQL.
Mac mysql server start command line password#
#Switching to the legacy password flowįor some clients (e.g. This article from the official documentation describes in detail, how you may reset your password on different systems. #Resetting the root user passwordįorgot the password of your root database server user? No worries, you can reset it!
Mac mysql server start command line how to#
You find detailed instructions on how to completely remove MySQL on Linux in this Stackoverflow thread. You also might want to get rid of all the related data - this article describes how that can be achieved. Go to the "MySQL" option and choose "Uinstall". If you installed MySQL via the official installer, you can uninstall it via the macOS "System Preferences". Thereafter, to clean up any remaining data, make sure you can see hidden folders and then delete the following folders: Go to "Programs and Features" and select "MySQL" => "Uninstall".
Mac mysql server start command line windows#
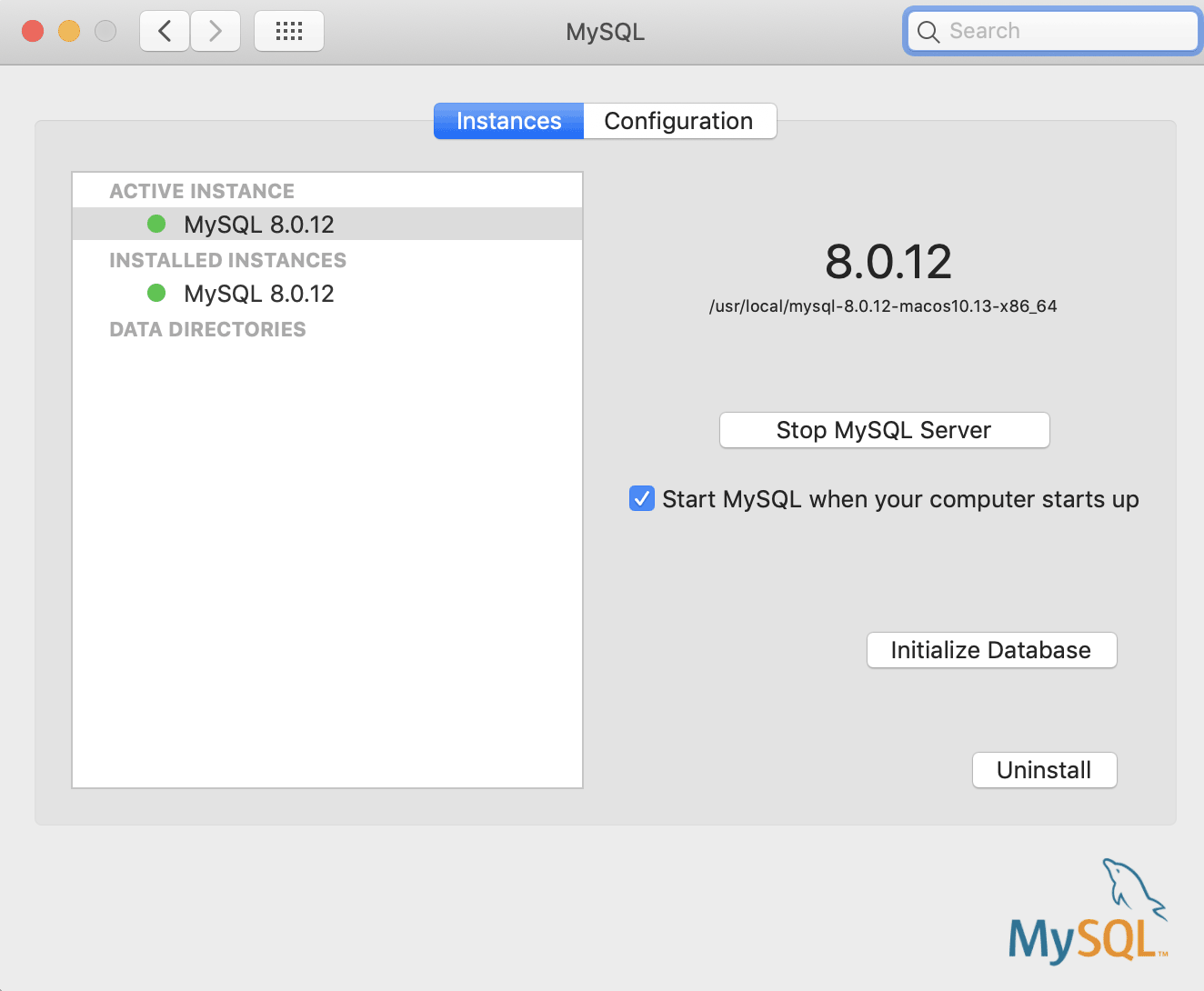
Once the server is stopped, you can uninstall MySQL via the Windows "Control Panel". To uninstall MySQL on Windows, make sure that your first stop the running server. To start a MySQL server on Linux, you can run the following command: /etc/init.d/mysqld startĪlternatively, you can also start a running background server service by running: service mysqld start #Uninstalling MySQL (Windows) #Starting a server (macOS)īesides that, you can also start the MySQL server via the macOS terminal: sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/rver start #Starting a server (Linux) It will prompt you for your password and start the server once you entered it. Start the running server by executing: mysqld Once you navigated into that path, you can run the mysqld command which is located there. You can find this executable in your installation directory inside the bin folder - for example C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin. You find more details here.Ī MySQL server can be started via the mysqld command which was installed on your system automatically. If you want to run the MySQL server as a service, you can start and stop it via the Windows services tool. That's all! You can thereafter restart the server if you want to. To stop a running MySQL server on Linux, you can run the following command: /etc/init.d/mysqld stopĪlternatively, you can also stop the running background server service by running: service mysqld stop If you dive into the "MySQL" option there, you can start and stop the MySQL server via this GUI.īesides that, you can also stop the MySQL server via the macOS terminal: sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/rver stop #Stopping a running server (Linux) If you installed MySQL via the official installer, you should have a new entry in your "System Preferences" (at the very bottom of the overview page). You can then also restart the server if you want to. It will prompt you for your password and shut down the running server once you entered it. Stop the running server by executing: mysqladmin -u root -p shutdown Once you navigated into that path, you can run the mysqladmin command which is located there. If you haven't added the bin path to your environment variable, you have to navigate into that bin folder via your system command prompt.įor example, this is how you could navigate into the installation path mentioned above: cd "\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin" You can optionally add the path to this bin directory to your Windows path environment variable (see this tutorial), so that you can access the tools inside this bin folder from anywhere on your system.

You find more details here.Ī running MySQL server can be stopped via the mysqladmin command which was installed on your system automatically. If you started the MySQL server as a service, you can start and stop it via the Windows services tool.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
